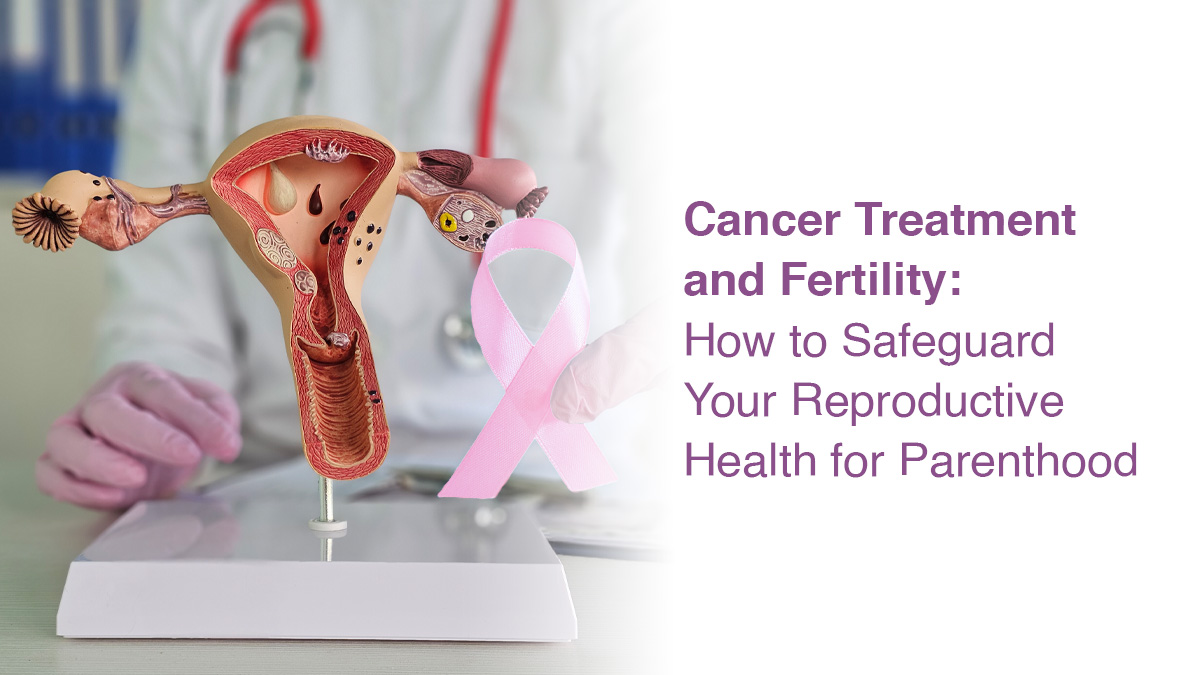
How do Cancer patients attain healthy parenthood?
How does Cancer impact Fertility?
- The disease itself can cause changes in the body by disrupting hormones needed for ovulation, and pressure effect on the reproductive organs thereby reducing fertility.
- Cancer Surgery: If ovaries, uterus, or testicles are removed as part of treatment, it can affect one’s ability to conceive.
- Radiation: Depending on the dose, duration, and site of radiation, one can even lose eggs in the ovaries leading to premature ovarian failure or sperms from the testes causing Azoospermia.
- Chemotherapy: Many of the drugs used in chemotherapy are harmful to the gonads and alkylating agents like Cyclophosphamide tops the list. These drugs can destroy the oocytes and deplete the follicular pool in women. It can lead to the reduction of sperm or germ cells in men leading to decreased fertility.
- Cancer and its treatment can also lead to menstrual disturbances in females and sexual dysfunction in males further affecting the chances of a successful conception.
- Age: Advancing age at diagnosis and treatment increases the risk of gonadal damage due to chemotherapy and radiation.
Fertility Preservation – A boon to achieve parenthood:
Fertility preservation is a process through which eggs, sperms, embryos, ovarian or testicular tissue are cryopreserved (stored in liquid nitrogen at an extremely low temperature of -196 degrees C) for future use. When cancer treatment gets completed and the male or female or the couple is ready for pregnancy, the frozen eggs/sperms/embryos can be thawed and IVF can be done to achieve pregnancy.
Types of Fertility Preservation:
a) Embryo Cryopreservation:
Here, mature eggs are retrieved from women with or without ovarian stimulation and fertilized with sperm through IVF. The embryo formed after fertilization is frozen. When the cancer treatment gets over and the woman is ready for pregnancy, the frozen embryo is thawed and implanted in the woman’s uterus to enable her in achieving motherhood. This method has the best chances of achieving pregnancy.
b) Sperm Freezing:
For men who have cancer, sperms can be retrieved before the treatment begins and frozen for later use. In prepubertal boys, testicular tissue can be frozen which can be implanted later and sperm extracted for use in ART.
c) Oocyte Cryopreservation:
This can be done during any time of the cycle depending upon the time available between diagnosis and the start of cancer treatment. Other factors like the patient’s age, time of the menstrual cycle, and type of cancer are taken into consideration at the time of planning the protocol. If possible, hormone injections are given to increase the number of developing follicles in the ovaries after which the eggs are retrieved from the women before cancer treatment and are frozen. The frozen eggs can be thawed and fertilized with sperm when she desires to have a pregnancy.
d) Ovarian Tissue Cryopreservation:
Here, a part or entire ovary is removed and frozen. This is useful in prepubertal girls and also in women where ovarian stimulation is not possible due to various reasons. After the treatment is completed and when the woman is ready for pregnancy, the ovarian tissue is reimplanted into the pelvic cavity or a heterotopic site. This procedure also has the advantage of helping patients get back their normal reproductive endocrine function, seen in almost 90% of cases as noted in a study. This tissue starts functioning and the eggs so produced by this transplanted tissue can be collected and used for fertilization.
Cancer need not take away one’s parenthood dream! Taking the right decision after a cancer diagnosis is of paramount importance that could save one’s reproductive potential for the future.


fill up the form to get a
Free Consultation
Avail 0% interest on EMI
All Procedures | No Upper Limit
How we reviewed this article:
- Current Version
- March 27, 2023 by Oasis Fertility