Influence of nutrition on female fertility

Author: Dr. Aparna Vishwakiran, Senior Consultant & Fertility Specialist
It has been already established that our health is influenced by the foods we consume and the nutritional value associated with them. The impact of poor dietary habits on overall health and fertility issues in specific is often overlooked. Unhealthy eating habits and unbalanced diets interfere with both male and female reproductive functions.
The role of nutritional diet in managing infertility is often underestimated. In addition to the medical treatment, a holistic approach like lifestyle modifications and adequate nutritional support will have beneficial effects on developing oocytes and sperm. This will help in improving and treating infertility in both men and women.
Female infertility is a prevalent medical and social condition among women of reproductive age worldwide.
It is caused due to various pathophysiological changes such as ovulation disorders, decline in ovarian reserve and egg quality, irregular menstrual cycle, hormonal imbalances, reproductive system condition, and other underlying chronic diseases.
Ovulation disorders and egg quality: One of the important biomarkers of female fertility is egg quality. The likelihood of an egg getting potentially fertilized depends on the quality of the ovum (egg). A woman’s capacity to conceive and future fertility depends on the number and quality of eggs present in the ovaries (ovarian reserve).
During a regular and healthy menstrual cycle an ovum is released, this process is called ovulation.
Any decline in the quality or number of the eggs or problem in the ovulation process leads to ovulatory infertility. Nutritional factors affect the maturation of oocyte, quality of embryos after fertilization and implantation.
PCOS and hormonal imbalances: It is an endocrine disorder characterized by the formation of cysts in the ovaries, hormonal imbalances, weight gain, inflammation, and irregular menstrual cycles. It is one of the major causes of infertility in women.
A proper balanced diet helps in easier management of PCOS.
Lifestyle-related factors such as abnormal body weight, nutritional disorders, smoking, obesity, alcohol consumption, etc. also cause fertility issues in women.

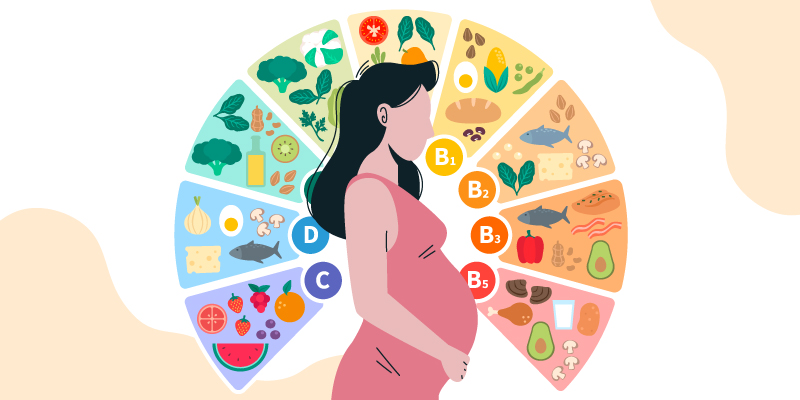
Foods to improve fertility:
-Whole grains provide sufficient nutrition and keep you full for a longer period without causing a blood sugar spike. Whole wheat, brown rice, barley, jowar, etc. are a few considerable options.
-Consuming legumes and lentils and preferably plant sources of protein reduces the risk of ovulatory infertility. Also, legumes are a good source of folic acid which aids in healthy embryo development. Protein intake is also known to play a positive role in lowering testosterone levels and maintaining the hormone levels in women affected with PCOS.
-Including sources of micronutrients such as zinc, iron, folic acid, and selenium also helps in maintaining follicular health and egg quality.
-Consume foods rich in folic acid or take folic acid supplements. Folic acid is associated with improved embryo quality, preventing birth defects, and reduced risk of ovulatory infertility.
-PCOS-related infertility can be managed by incorporating seeds such as flax seeds, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, and sunflower seeds. The phytoestrogens in these seeds help in regularizing hormonal levels and irregular menstrual cycle.
-Vitamin C-rich fruits and berries such as raspberries, strawberries, and blueberries are antioxidant-rich foods, their anti-inflammation properties help with PCOS-related infertility.
-Omega 3 fatty acids help in preserving fertility and also aids in the production of good quality eggs. Fish, eggs, dry fruits, plant oils, and nuts are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids.
-Steer clear from processed food, sugary and alcoholic beverages, and refined flour food products.
-Also, remember that an overload of carbohydrates and fats might have a negative effect on ovulation.
In conclusion, moderation is the key, and do not overeat or follow a strict diet. An enriched but balanced diet with proteins, fats, carbohydrates, antioxidants, minerals, and vitamins is highly beneficial for the optimal functioning of the female reproductive system and reducing the risk of infertility.