Infertility: Causes, Types
Infertility or inability to conceive could be due to any issue, either in the male or female partner or in both of them. A proper fertility evaluation of the couple can help in finding the real cause and enable the fertility specialist to devise a specific treatment plan accordingly.
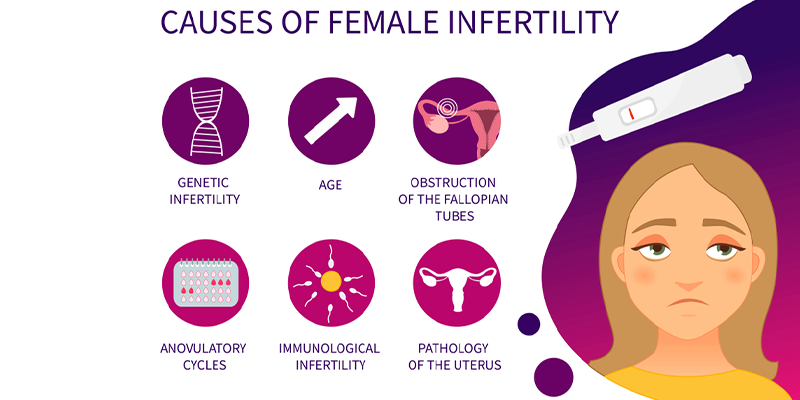
Infertility causes in Female:
- Ovulatory disorders
- Problems in the fallopian tube
- Problems in the uterus
- Endocrine disorders like thyroid and prolactin
- Endometriosis and adenomyosis
- Obesity
A. Disorders of ovulation:
Any imbalance in women’s reproductive hormones can cause ovulation disorders. Some of the ovulation disorders are as below:
- PCOS: PCOS/Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is characterized by the presence of excess levels of androgens (male hormone) leading to ovulatory disturbances. It is one of the most common causes of infertility in women. Symptoms that can lead to infertility in female include irregular periods, acne, excess hair growth, weight gain, etc.
- Primary Ovarian Insufficiency/premature ovarian failure: In some women, ovaries stop functioning before 40 years due to various reasons.
- Genetic causes: Chromosomal disorders like Turner syndrome, fragile X syndrome, etc. lead to premature ovarian failure.
B. Problems in the Fallopian tube:
The fallopian tube is a part of the female reproductive system where fertilization of egg and sperm happens. But there are several issues in the fallopian tube that can hamper one’s fertility. Some of the reasons are:
- Absent fallopian tubes (Tubal aplasia)
- Infections like Tuberculosis
- Sexually transmitted diseases leading to Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Previous surgery in pelvis/abdomen
- Appendicitis
- Hydrosalpinx (fluid accumulation in the fallopian tube)
C. Problems in the Uterus:
- Fibroids
- Unusually shaped uterus
- Endometrial pathology like thin endometrium, polyps
D. Endometriosis and adenomyosis:
Endometriosis is a condition wherein endometrium (lining of the uterus) grows in places other than the uterus like the pelvis/abdomen. It can cause heavy painful periods and also impact fertility due to a decrease in the ovarian reserve, adhesions, etc.
Adenomyosis affects the endometrial function and receptivity thereby reducing the implantation potential and chances of pregnancy.
The above reasons can hamper fertility.
Diagnosis of Female Infertility:
- Physical Examination
- Ultrasound
- Hormone tests including ovarian reserve testing
- Hysterosalpingography
- Hysteroscopy
- Laparoscopy
- Genetic testing
Treatment of Female Infertility:
- Ovulation induction in cases of anovulation
- Laparoscopic/Hysteroscopic surgery is done to correct any uterine abnormality, cornual tubal block, fibroids or endometrial polyp
- Assisted reproductive technologies like IUI, IVF when required can help women conceive
Infertility causes in Male:
Male infertility can happen due to a variety of reasons:
- Problem in the production of sperm: Proper growth and formation of the male reproductive system are highly essential for normal sperm production. Any problem in sperm production can cause infertility.
- Problem in sperm transportation: Ducts that carry sperms may have blockage due to surgery, congenital disorders, or infections.
- Problems in sperm motility: If the sperms have abnormal motility, they may not be able to reach the egg.
- Infection: Infections like sexually transmitted diseases can hinder sperm production and also sperm motility.
- Ejaculation issues: Many health conditions like Diabetes, bladder surgery, medications, etc. can cause problems in ejaculation.
- Cancer: Cancer & treatments like chemotherapy, and radiation affect fertility by affecting both libido and sperm quality.
- Genetic defects: Cystic fibrosis, Klinefelter’s Syndrome, and other genetic disorders can affect sperm production and transportation.
- Antisperm antibodies: Some immune cells attack sperms mistaking them for harmful invaders.
- Undescended testicles: For some men, the testicles fail to descend before birth leading to infertility.
- Varicocele: An abnormal enlargement of veins in the scrotum (the bag covering the testicles) is called varicocele and it can result in low sperm production and reduced sperm motility.
- Chemicals/X-rays: Exposure to pesticides, toxins, and heat can lead to low sperm count.
- Smoking: Men who smoke have low sperm count and motility and declined sperm quality.
- Obesity: Being overweight can affect hormone balance and also affect fertility.
Symptoms of Infertility in Men:
- Mostly asymptomatic
- Changes in sexual desire
- Small testicles
- Pain/swelling in the testicles
Diagnosis of Male Infertility:
Some of the below tests are done to diagnose male infertility:
- Physical Examination
- Semen Analysis
- Ultrasound- scrotal, transrectal
- Hormone tests
- Genetic Tests
Treatment of Male Infertility:
- Medical management in cases of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, reduced sperm count and motility in the form of hormones, antioxidants, etc.
- Advanced treatments like IUI, IVF/ICSI can be used to help men overcome infertility and attain fatherhood.
- Sperm retrieval techniques like TESA, Micro-TESE, and sperm separation procedures like MACS, Microfluidics are available which can improve fertility.
Infertility Types:
- Primary Infertility – When the couple is unable to conceive even after 1 year of trying, it is called primary infertility.
- Secondary Infertility – When the couple is unable to conceive for the 2nd time (after successfully having a pregnancy), it is said to be secondary infertility.
Fertility declines with age and hence fertility evaluation is very important for both male and female partner as early diagnosis and intervention can help the couple overcome infertility and achieve their parenthood dream. Anybody who is planning to conceive has to follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, quit smoking and alcohol and have a proper sleep pattern that will boost the chances of conception.


fill up the form to get a
Free Consultation
Avail 0% interest on EMI
All Procedures | No Upper Limit
How we reviewed this article:
- Current Version
- November 14, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- October 31, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- October 28, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- October 21, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- October 19, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- October 18, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- October 6, 2022 by Oasis Fertility
- September 20, 2022 by Oasis Fertility